What Is Inflammation and Why Should You Care?
Inflammation is your body’s natural defense mechanism. When you cut your finger or catch a cold, your immune system responds by sending white blood cells to heal and protect. This type of acute inflammation is healthy and necessary.
But when inflammation becomes chronic, lingering silently in the background, it turns from healer to enemy. Chronic inflammation is now considered a major contributor to many serious diseases — from heart disease and diabetes to cancer, depression, and even Alzheimer’s.
Understanding how inflammation works — and how to manage it — is one of the smartest steps you can take for long-term health.
For more deep dives into important wellness topics, visit:
https://healthmanual.net/healthtips/
1. Acute vs Chronic Inflammation: What’s the Difference?
Acute inflammation is short-term and easy to recognize. It’s what happens when:
- You sprain your ankle → it swells
- You catch a virus → you develop a fever
- You get a cut → the area turns red and warm
This type of inflammation is the body’s way of healing.
But chronic inflammation is different. It occurs inside the body, often without obvious symptoms. It may be triggered by:
- Poor diet
- Chronic stress
- Lack of sleep
- Environmental toxins
- Long-term infections or autoimmune reactions
Over time, this low-grade, persistent inflammation damages healthy tissue and contributes to disease progression.
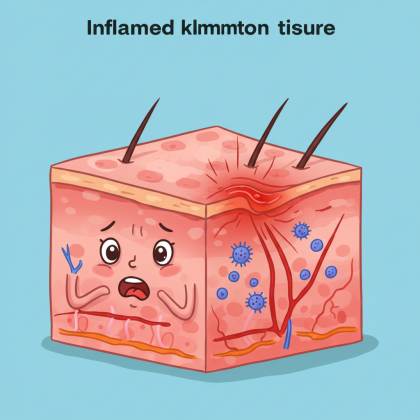
2. Diseases Linked to Chronic Inflammation
You might be surprised to learn how many health conditions are rooted in inflammation. Here are some of the most common:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Inflammation damages blood vessel linings, leading to atherosclerosis (plaque buildup), which can result in heart attacks or strokes.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Chronic inflammation interferes with insulin signaling, contributing to insulin resistance.
- Cancer: Long-term inflammation creates an environment that supports tumor growth and DNA damage.
- Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis is a classic example of the immune system attacking joints due to misdirected inflammation.
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Brain inflammation has been linked to neurodegeneration and memory decline.
- Depression: New research shows that inflammatory cytokines can affect brain chemistry and mood regulation.
These links show how inflammation is often a root cause, not just a symptom.
3. How Do You Know If You Have Chronic Inflammation?
Chronic inflammation doesn’t always produce obvious symptoms. But some warning signs include:
- Persistent fatigue or brain fog
- Joint or muscle pain
- Digestive issues (bloating, constipation, diarrhea)
- Frequent colds or infections
- Skin problems like acne, eczema, or psoriasis
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
The most accurate way to check for inflammation is through blood tests, such as:
- C-reactive protein (CRP)
- ESR (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate)
- Fibrinogen
- IL-6 or TNF-alpha levels
These are often ordered if your doctor suspects chronic inflammatory issues.
4. The Role of Diet in Inflammation
What you eat is one of the biggest influences on inflammation — either reducing it or fueling it.
Pro-Inflammatory Foods (Avoid or Limit)
- Refined sugars (sodas, pastries)
- Processed meats (sausages, bacon)
- Refined carbs (white bread, white rice)
- Deep-fried foods
- Trans fats and hydrogenated oils
- Excessive alcohol
These foods promote oxidative stress and can overstimulate the immune system.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods (Add More of These)
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines)
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale)
- Berries (blueberries, raspberries)
- Turmeric (with black pepper)
- Olive oil
- Green tea
- Nuts and seeds (especially walnuts and flaxseeds)
A Mediterranean-style diet is one of the best evidence-backed eating plans to reduce inflammation.
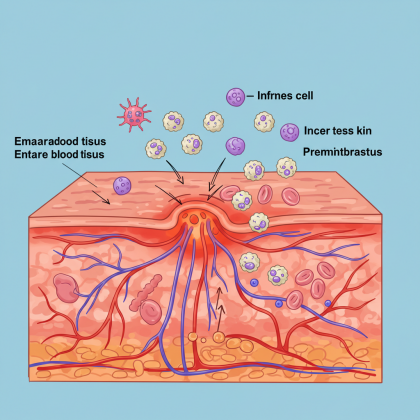
5. Lifestyle Factors That Affect Inflammation
Diet is key — but it’s not the only factor. These daily habits also play a major role:
Get Enough Sleep
- Aim for 7–9 hours of uninterrupted sleep
- Poor sleep increases inflammatory markers like CRP
Manage Stress
- Chronic stress = chronic inflammation
- Mindfulness, meditation, and breathing exercises can lower cortisol
Exercise Regularly
- Moderate activity reduces inflammation over time
- Avoid overtraining, which can temporarily spike it
Avoid Toxins
- Reduce exposure to pesticides, air pollution, and chemical household cleaners
- Switch to natural personal care products where possible
Even gum disease and poor dental hygiene can increase systemic inflammation — so don’t skip brushing and flossing.
6. Supplements That May Help
Some natural supplements can help regulate inflammation:
- Omega-3 fatty acids: From fish oil or algae oil
- Curcumin: The active compound in turmeric
- Vitamin D: Especially for those with low blood levels
- Probiotics: For gut health support
- Magnesium: Plays a role in inflammatory pathways
Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting supplements, especially if you’re taking medications.
7. Long-Term Benefits of Reducing Inflammation
Lowering chronic inflammation isn’t just about avoiding disease. It can also:
- Improve energy and mood
- Promote clearer skin
- Support healthy aging
- Reduce joint and muscle pain
- Improve digestion and metabolism
Ultimately, inflammation is a signal — your body is trying to tell you something. If you respond with healthier habits, the benefits ripple across every part of your life.
Final Thoughts: Make Anti-Inflammatory Living Your Lifestyle
Chronic inflammation is often called “the silent killer” for a reason. You won’t always feel it — but it can be undermining your health daily.
The good news? You don’t need extreme diets or drastic measures. With consistent effort in food, sleep, stress, and movement, you can reduce inflammation and build a healthier future.
Ready to take control of your health? Explore more trusted wellness content here:
https://healthmanual.net/healthtips/

Hi, I’m Hibiki — the writer behind HealthManual.net.
I cover health insurance news, wellness tips, and insightful analysis of pharmaceutical and healthcare stocks. My goal is to simplify complex topics and make health and finance information more accessible to everyone.
Thanks for reading — I hope you find the content helpful and reliable.